As I discussed in my first blog article, trust and responsibilities play an important role in cloud computing. Compliance with data protection and information security already present various challenges to the operational and administration teams from the time of operating on-premises services and constellations.
If we include cloud computing, we have a third party involved, namely the cloud provider. The level of complexity increases and matters such as data location and the interplay of the individual cloud services come to the fore. But let’s start at the beginning:
In this blog article I’ll highlight the differences between data protection and information security and then focus on encryption. So climb aboard, fasten your seat belt and enjoy the ride!
“Maybe it’s two miles. Hang on.“ – Korben Dallas
The fifth element
Besides identity & access management, threat protection, network security, and security management, data & information protection forms the fifth pillar the fifth element of the pillars of Security in Azure.
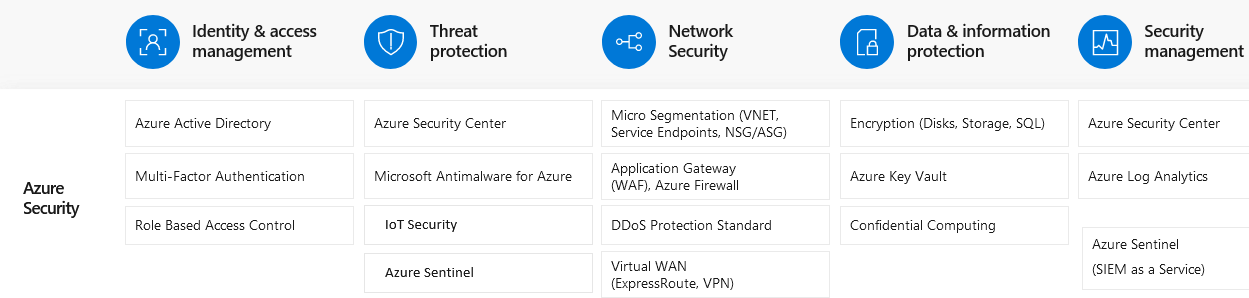
Source: Microsoft/Own representation
But before we take the exit towards encryption and the Azure Key Vault, let’s look at the difference between data protection and information security. It’s important to bear in mind that there is an intersection of topics as well as flowing transitions.
The most distinctive difference between data protection and information security is that data protection is subject to strict legislation while information security lies within the discretion of the organization. Data protection safeguards personal data and the right to informal self-determination; in other words, it governs how and whether personal data may be processed in the first place.
Information security imposes technical and organizational measures so as to secure all data and business processes in the systems of the organization. Data security accordingly forms part of information security and is therefore closely related to data protection. Examples of information security are the measures necessary for protecting internal matters.
In sum, we may say that data protection and information security are inseparable!
Now let’s continue our ride and look at how information security and data protection can be safeguarded in Azure.

© 2021 MakerBot Industries, LLC
“Leeloo Dallas mul-ti-pass“ – Leeloo
Multi-pass – managed key
Encryption enables the transformation of information for subsequent decryption and therefore reading by authorized entities. Data in “plain text” is converted to a cryptogram linked to a key, and rendered readable only by means of this key. Microsoft Azure offers a variety of encryption types and information or systems to be encrypted.
Azure Server-Side Encryption:
Azure SSE encrypts managed disks and storage resources, and protects data at rest. By default, encryption employs platform-managed keys, with 256-bit AES encryption being the case.
When using platform-managed keys, Azure automatically controls encryption and decryption. For organizations that can trust Azure in terms of compliance and that are not regulated more strictly, this default configuration suffices for a start.
Should stricter requirements apply, resources can be protected with an organization’s internal keys. The keys to the encrypted resources must then be made accessible. The Azure Key Vault affords this accessibility.
Azure Key Vault:
The Azure Key Vault serves the secure storage of and access to confidential information. In the Azure Key Vault you can store API keys, passwords, certificates or keys, for example. Access to the Key Vault is controlled via ACL through identity authentication and access restrictions. Accessing can be read out through detailed logs.
Azure SQL encryption
You can also encrypt SQL databases in Azure. Two different technologies are available for this purpose:
- Transparent Data Encryption (TDE)
- Always Encrypted
TDE encrypts the complete database using an AES algorithm. This encryption protects data at rest against hardware theft and illegal data recovery, for example. Once loaded to the memory, data can be read by any authorized entity (such as administrators or applications). Always Encrypted (a client-side encryption measure) additionally encrypts data “in use”.
Should higher protection be required, Always Encrypted is the solution for performing operations on encrypted SQL databases.
Combined with the aforementioned encryption options, the Azure Key Vault ensures data & information security when operating resources in Azure.
“Boooooooom ba da booom“ – Leeloo
Besides the encryption of data and systems, other factors related to data protection and information security also play a role. Cloud-provider data center locations, data classification, the design of new processes for meeting the requirements on cloud computing, assurance of the requisite availability and access regulations together ignite veritable fireworks of complexity.
Cloud computing, data protection, and information security are not mutually exclusive. Given the right measures and technologies, it’s possible to utilize resources and services in the context of cloud computing. Even if we’ve only seen just a few examples of the many possibilities nowadays, you get the picture of the great potential!
Now we’ve reached the end of our sightseeing tour. Unfasten your seatbelt, enjoy the day and don’t forget your multi-pass on the back seat!
Author: Dominic Iselt, IT Security Engineering Expert
